
- #HOW DO YOU CREATE AVECTOR WITHOUT A LOOP IN R MANUAL#
- #HOW DO YOU CREATE AVECTOR WITHOUT A LOOP IN R SOFTWARE#
R are essentially ephemeral, written for a single piece of data It has developed rapidly, and has been extended by a R is very much a vehicle for newly developing methods of interactiveĭata analysis. Very specific and inflexible tools, as is frequently the case with other Planned and coherent system, rather than an incremental accretion of The term “environment” is intended to characterize it as a fully (Indeed most of the system suppliedįunctions are themselves written in the S language.) Which includes conditionals, loops, user defined recursive functions and
#HOW DO YOU CREATE AVECTOR WITHOUT A LOOP IN R SOFTWARE#
R is an integrated suite of software facilities for data Next: Related software and documentation, Previous: Introduction and preliminaries, Up: Introduction and preliminaries 1.1 The R environment Until all the preceding sections have been digested. See Graphics, which can be read at almost any time and need not wait Many users will come to R mainly for its graphical facilities. This should give some familiarity with the style of R sessionsĪnd more importantly some instant feedback on what actually happens. Most R novices will start with the introductory session in AppendixĪ. In this way, and for being a supporter of R from way back.Ĭomments and corrections are always welcome. We would like to extend warm thanks to Bill Venables (and David Smith)įor granting permission to distribute this modified version of the notes R and S programs, and expanded some of the material. Have made a number of small changes to reflect differences between the Smith when at the University of Adelaide. This introduction to R is derived from an original set of notesĭescribing the S and S-PLUS environments written in 1990–2 byīill Venables and David M. Next: Introduction and preliminaries, Previous: Top, Up: Top Preface
#HOW DO YOU CREATE AVECTOR WITHOUT A LOOP IN R MANUAL#
Permission is granted to copy and distribute translations of this manual Manual under the conditions for verbatim copying, provided that theĮntire resulting derived work is distributed under the terms of a Permission is granted to copy and distribute modified versions of this Manual provided the copyright notice and this permission notice are Permission is granted to make and distribute verbatim copies of this This manual provides information on data types, programming elements,Ĭopyright © 1992 W. (linear and nonlinear modelling, statistical tests, time seriesĪnalysis, classification, clustering. It provides a wide variety of statistical and graphical techniques System, which was developed at Bell Laboratories by John Chambers et al. This is an introduction to R (“GNU S”), a language and environment for 12.6.1 PostScript diagrams for typeset documents.12.4.2 Temporary changes: Arguments to graphics functions.12.4.1 Permanent changes: The par() function.12.1.4 Arguments to high-level plotting functions.

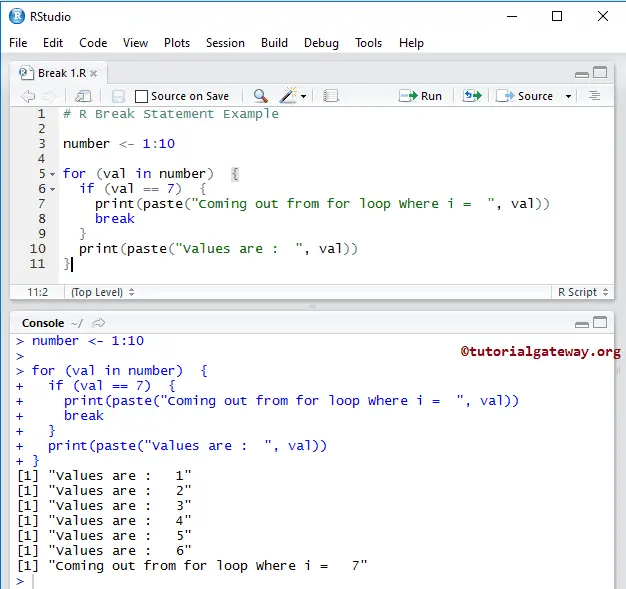
10.6.2 Dropping all names in a printed array.10.6.1 Efficiency factors in block designs.9.2.2 Repetitive execution: for loops, repeat and while.9.2.1 Conditional execution: if statements.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
